
When a secure port is in the error-disabled state, you can bring it out of this state by entering the errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation global configuration command, or you can manually re-enable it by entering the shutdown and no shut down interface configuration commands.
shutdown-a port security violation causes the interface to become error-disabled and to shut down immediately, and the port LED turns off. 
An SNMP trap is sent, a syslog message is logged, and the violation counter increments. In this mode, you are notified that a security violation has occurred.
restrict-when the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the maximum limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses to drop below the maximum value or increase the number of maximum allowable addresses. The protect mode disables learning when any VLAN reaches its maximum limit, even if the port has not reached its maximum limit. We do not recommend configuring the protect violation mode on a trunk port. You are not notified that a security violation has occurred. 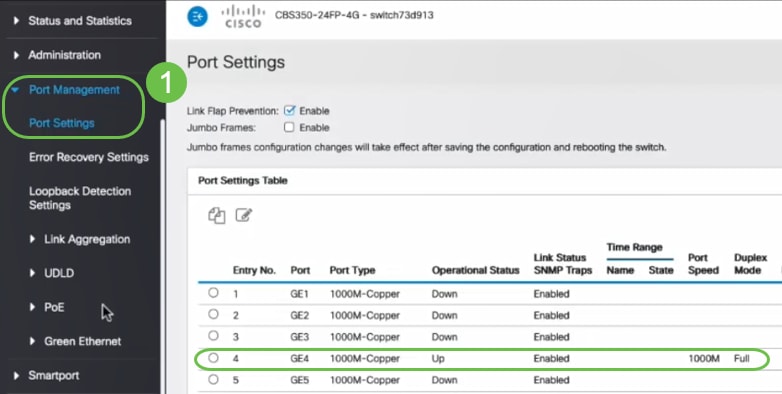
protect-when the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the maximum limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses to drop below the maximum value or increase the number of maximum allowable addresses.You can configure the interface for one of three violation modes, based on the action to be taken if a violation occurs:
 An address learned or configured on one secure interface is seen on another secure interface in the same VLAN. The maximum number of secure MAC addresses have been added to the address table, and a station whose MAC address is not in the address table attempts to access the interface. It is a security violation when one of these situations occurs:
An address learned or configured on one secure interface is seen on another secure interface in the same VLAN. The maximum number of secure MAC addresses have been added to the address table, and a station whose MAC address is not in the address table attempts to access the interface. It is a security violation when one of these situations occurs:







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
